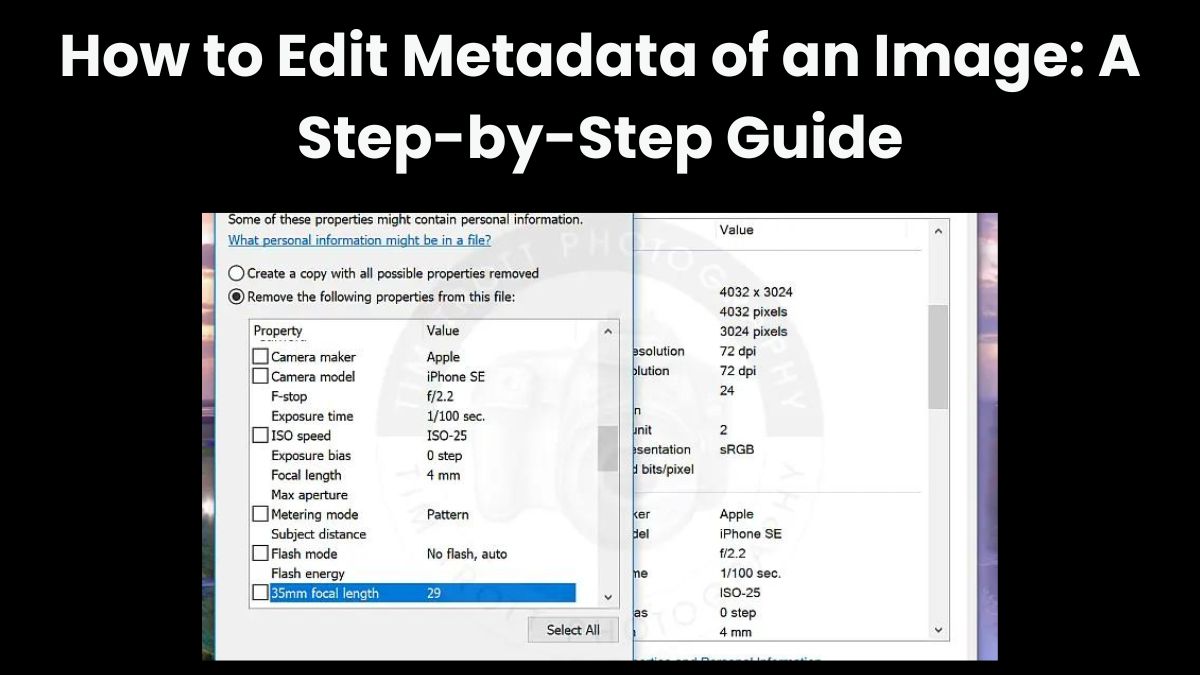
Images carry a lot more information than what meets the eye. Each image file has metadata, beyond its visual content. This is extra info embedded in the file. It includes the camera model, exposure settings, location, date of creation, and more. Editing this metadata is important for many reasons. It helps to organize your image library, remove location data for privacy, and optimize images for SEO.
This blog post will cover image metadata. We will explain why you might want to edit it. Then, we will show you how to use the FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor to do so.
What is Image Metadata?
Image metadata refers to information that is embedded in an image file. It is in the image itself. It can provide technical details and other data, like keywords and descriptions. Metadata can typically be divided into three main categories:
- EXIF Data: This includes camera settings like shutter speed, aperture, ISO, and the date and time the photo was taken. Some cameras and smartphones also record GPS coordinates, embedding location data in the image.
- IPTC Data: Information such as captions, credits, copyright notices, and other textual details related to the image.
- XMP Data: Metadata stored using the XML format, which is more flexible and can include both EXIF and IPTC data.
Why Edit Image Metadata?
There are several reasons why someone might want to edit the metadata of an image. Here are some common use cases:
1. Improve SEO
If you manage a blog, website, or social media account, optimizing your images for search engines is crucial. Adding metadata, like keywords and titles, can help search engines understand your image. This can improve your SEO rankings. Search engines can’t “see” images but rely on metadata to categorize and rank them in search results.
2. Protect Your Privacy
Modern cameras and smartphones can embed GPS coordinates in images. Anyone who views the metadata can see exactly where the photo was taken. Editing or removing this location data is a great way to protect your privacy, especially when sharing images online.
3. Organize Your Image Library
Editing image metadata can also help you organize large collections of images. By adding custom tags, descriptions, and dates, you can make your images easier to find, categorize, and retrieve when needed.
4. Copyright and Licensing
Photographers and digital artists often use metadata to embed copyright and licensing info in their image files. This makes it clear who owns the image and what rights are associated with its use.
5. Correct Incorrect Data
Sometimes the automatic metadata embedded by a camera or software may be incorrect. For instance, the time and date might be wrong, or location data may need to be updated. In such cases, editing the metadata can correct these inaccuracies.
How to Edit Metadata of an Image Using FileProInfo
Editing image metadata used to require specialized software. Now, you can easily do it online for free with the FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor. This tool allows you to add, edit, or remove metadata from image files, including popular formats like JPG. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
Step 1: Visit the FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor
Go to the FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor page. Navigate to FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor. This tool lets you edit metadata in a secure, user-friendly place. No registration or installation is needed.
Step 2: Upload Your Image
Once on the page, you will find an option to upload your image file. You can drag and drop the file into the box. Or, click “Choose File” to select the image from your device. The tool supports a variety of image formats, including JPG, PNG, GIF, and more.
Step 3: Edit the Metadata
After uploading your image, the tool will display the metadata associated with your file. You can now proceed to edit the various fields available:
- Title: Add a descriptive title for your image.
- Description: Provide a brief description of the content in the image.
- Keywords: Add relevant keywords that describe the image. These can be helpful for SEO purposes.
- Copyright: Include any copyright information or licensing terms.
- Location Data: If the image contains GPS coordinates, you can choose to edit or remove this information.
- Camera Settings: Adjust or correct details such as the camera model, ISO, aperture, and shutter speed.
Step 4: Save the Changes
Once you’ve made the necessary changes to the metadata, click the “Save” button. FileProInfo will process your image and apply the changes to the metadata.
Step 5: Download the Edited Image
After processing, you will be prompted to download the edited image file with updated metadata. You can now use this image for your personal or professional needs.
Features of FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor
The FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor is one of the best tools for editing image metadata online. It has several features that make it so. Here’s a quick rundown of its benefits:
- No Software Installation: Since the tool is web-based, you don’t need to download or install any software. It works right from your browser.
- Free and Easy to Use: FileProInfo is 100% free to use, with no hidden costs or subscription fees. Plus, the interface is intuitive and beginner-friendly.
- Privacy and Security: The tool is designed with security in mind. Your files are processed on secure servers, and all uploaded images are automatically deleted within 1 to 24 hours after processing, ensuring your privacy.
- Supports Multiple Formats: Whether you’re working with JPG, PNG, or other common image formats, FileProInfo has you covered.
- Cloud-Based Processing: The metadata editing is performed on the cloud, meaning it doesn’t use up your system resources or require a powerful computer.
- SEO-Friendly: Add titles, descriptions, and keywords to optimize your images for search engines and boost your website’s visibility.
Best Practices for Image Metadata Editing
When editing image metadata, follow these best practices. They will optimize your images for search engines and make them easy to organize.
1. Use Descriptive Titles
Choose a descriptive title that accurately reflects the content of the image. This not only helps in better organization but also assists with SEO. A title like “Golden Sunset Over the Mountains” is far more effective than “IMG_001”.
2. Add Relevant Keywords
Include keywords that are relevant to the image and what you want it to be associated with. Keywords should be specific. But, avoid keyword stuffing; it can hurt your SEO.
3. Remove Sensitive Information
Be cautious about the personal data embedded in image files, such as GPS coordinates. If you’re sharing images online, removing location data can protect your privacy.
4. Use Consistent Metadata Across Similar Images
If you have a collection of similar images, keep your metadata consistent. This will make it easier to organize and retrieve the images later on.
5. Regularly Update Metadata
If your image library grows, regularly update the metadata. It should reflect any changes or new info you want to add.
Conclusion
Editing image metadata is vital for anyone who works with digital images. This includes personal use, professional work, and SEO. Use the FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor to edit or remove image metadata. It’s free, online, and requires no software installation.
FileProInfo is a secure, easy-to-use tool for your needs. It can optimize images for better search rankings. It can remove location data for privacy. It can add info for better organization.
Try the FileProInfo Image Metadata Editor. Control your image files’ metadata with a few clicks!